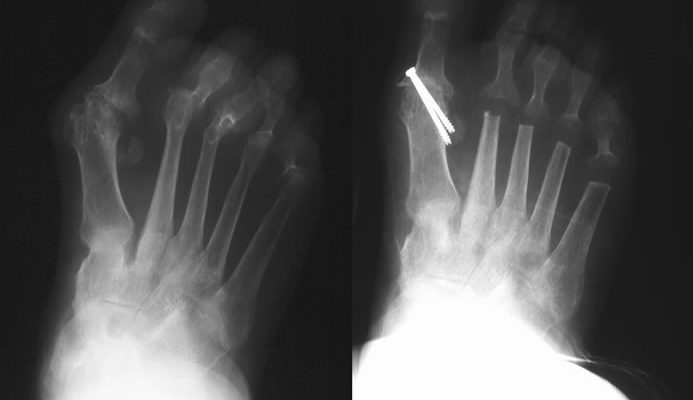
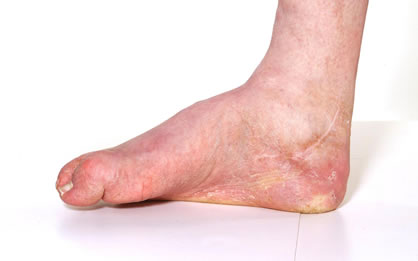
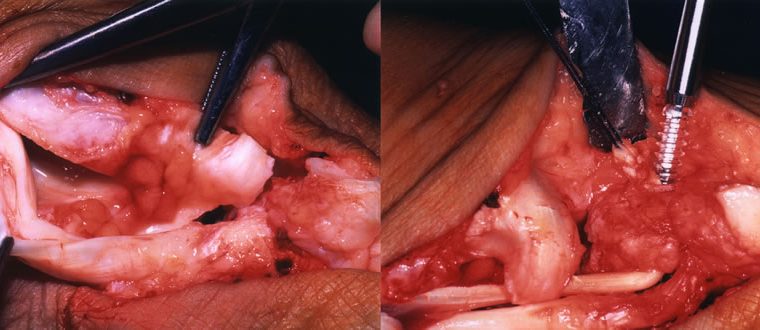
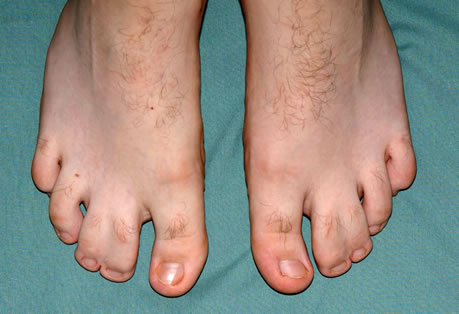
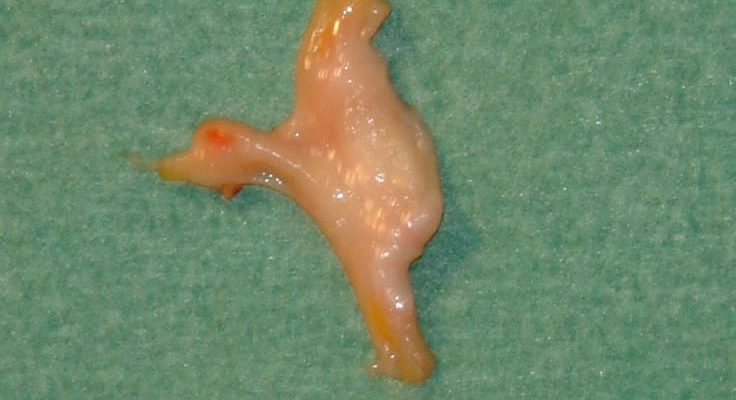
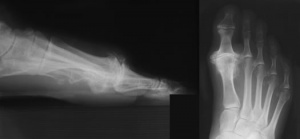
Osteochondritis of the Talus
Osteochondritis is a painful disease of the joint where the cartilage or bone in a joint is inflamed. It is a condition that can affect many of the bones and joints of the foot. Osteochondritis of the talus affects the supero-Iateral and supero-medial corners of …